
Multilingual Data & Knowledge
How can semantic technologies help to revolutionize the way we do business?
Victoria Penker and Angela DaSilva
If we have learned anything during the Covid-19 pandemic, it is that business as usual is a concept of the past. The way we manage and think about businesses has fundamentally changed as a result of the global crisis and political instability.
In a world of ever-evolving innovation, new technologies, and business models are not only disrupting the way corporations used to operate but also transforming the way we regard product, supply, and customer relationships.
Learning how to scale up operations during these times is a necessary skill that both employees and managers will have to adapt to. Digital technologies are a crucial component of this ongoing process and hold the potential to build a resilient organization that thrives despite uncertainty.
The workplace revolution
Companies have had to quickly adopt new ways to maintain business operations, and they began to recognize the value of a digital workspace that reflects modern work styles, maturing technologies, and new communication approaches.
Following the success of remote work during the pandemic, many businesses are already in the process of transitioning from traditional to flexible workplaces.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to enhance service operating journeys, streamline activities, and eliminate vulnerabilities, enabling decision-makers to facilitate internal and external procedures. As part of this process, the usage of semantic technologies is growing in popularity within the context of digital transformation and has become a multifarious powerhouse of corporate operations. Business leaders now have the task of turning data into knowledge and building a solid basis for their company.
The Semantic Web Company
Founded in 2004, the Vienna-based Semantic Web Company is the vendor of the PoolParty Semantic Suite, a complete and advanced semantic middleware on the global market. PoolParty Semantic Suite leverages machine learning, natural language processing, and graph technologies to enrich and interlink enterprise data. It uses innovative means to help organizations build and manage enterprise knowledge systems as a basis for their AI strategy.
Content and digital asset management are of particular interest to companies these days, where semantic technologies are being sought out to add an intelligent layer to workflows that have been broken down by hybrid workspaces. To combat these issues, the PoolParty approach to content management is making content more accessible to both internal and external stakeholders. The approach begins with a taxonomy in the PoolParty Thesaurus Server, and encompasses the following:
Text analytics and concept tagging
Using natural language processing, PoolParty enables the extraction of semantic concepts to mitigate linguistic challenges commonly found in unstructured text. If we take language ambiguity, for example, apple is a fruit, but it is also the name of a technology company; while humans understand the difference, a machine cannot process it unless it is trained.
taxonomy
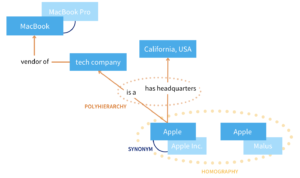
Semantic text mining can distinguish such occurrences based on a taxonomy and the local context of the ambiguous concepts. Representing a specific knowledge domain, the taxonomy helps to define parameters for which entities can be extracted and synced back to the taxonomy before they are sorted into their corresponding concept schemes and classes. The benefit to maintaining semantic tagging in a taxonomy is the consistency it provides through its hierarchical structure and controlled vocabularies.
Furthermore, semantic concepts in themselves are a uniquely powerful alternative to keyword-based tagging. Semantic concepts ensure that documents are tagged with more than just a singular term, but rather its synonyms and multilingual/alternative labels. In this way, a product like the Apple MacBook can be bundled with words like laptop, notebook, and computadora in a Spanish subsidiary, or by its versioning like the MacBook Pro or MacBook Air.
Semantic search and recommender systems
When content is tagged with concepts, the chief benefit is a vastly enhanced search engine. Semantic search is a solution that leverages the work already done with advanced text mining and concept tagging to take on all the linguistic challenges from a search perspective.
Using the MacBook example from above, if a technical writer enters MacBook in the search field, the semantic search engine would find all the articles tagged within that concept. The technical writer who wishes to update all the relevant Help articles with crucial product information can be assured that no articles are missed in the process.
Similarly, the semantic search engine can interpret and gather results based on the user’s natural language. Consider the MacBook example from the customer side, where the customer wants to upgrade to a better internal processor but first needs to understand the size of their current one; they get a technician on the phone to help with the upgrade process. The user can search with terms they understand and use daily (e.g. specs of an Apple notebook), but their search will also automatically expand to include terms that are synonymous with other parties (i.e. support teams, MacBook Pro specifications). As the semantic search engine draws upon natural language and the semantics concepts, users can easily find the information they need regardless of their input.
This is especially helpful for recommender systems, which give users’ results that are precisely tailored to their search query and can suggest “further reading” content to get a deeper dive into a product explanation. The semantic recommender system does not simply recommend “more of the same,” but enriches the experience with additional information.
A semantic recommender system is unique for its ability to make complex pairings between a user request and the content at hand. The following example is pulled from the PoolParty Wine + Cheese Sample Recommender Demo, which illustrates how a semantic knowledge model in the background helps to establish connections between two different, products (cheese and wine) that complement each other based on their relation to each other in a knowledge graph.
recommender
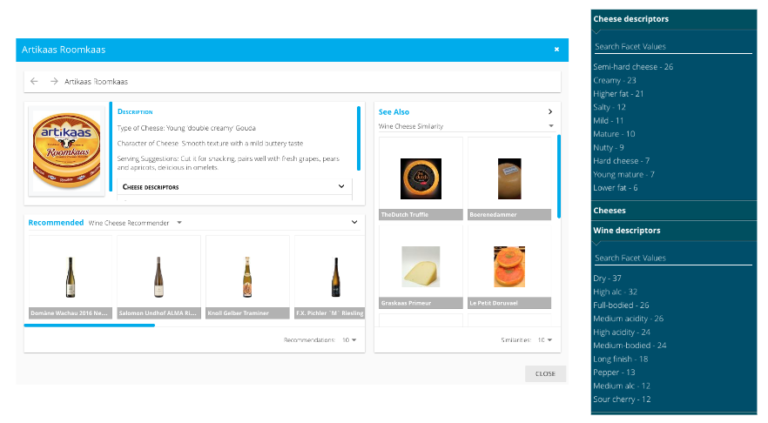
The facets used in the demo represent the different descriptors that are then weighed against each other to make the flavour pairings.
Increasing findability across digital workspaces
All this is to point towards having better findability and reusability of content, which companies often lack today. Many companies use traditional content management systems that have weak metadata and even poorer user search.
PoolParty Semantic Suite provides a solution with the Intelligent Content Hub, which goes beyond simple curation and maintenance of business assets and adds a much-needed layer of intelligent search and recommendations. As the most complete Semantic AI middleware on the market, one of PoolParty’s chief principles is being highly integrable with existing systems to provide semantic search and recommendations.
Within the Intelligent Content Hub, a company can connect its content infrastructure to PoolParty to enable the semantic layer. The semantic layer spans an umbrella over existing content and data management systems to link them together (Knowledge graphs), and essentially “push out” consistency and findability (concept tags and semantic search) back into a hub.
To take full advantage of the hub format, more and more tools can be added to the platform such as an autosuggestion writing tool, a translation engine, a chatbot, and so on. All these platforms and capabilities can come together to ensure that stakeholders have access to data and documents.
The enterprise knowledge graph sits at the center of all these siloed systems and tools, enabling the interoperability of them. When this is in place, companies can use the content hub to its full capabilities, leveraging the relations defined in the knowledge graph and the advanced search performance to access data and content more efficiently.
PoolParty is a tool that does not solely appeal to technicians and knowledge engineers but can also benefit content creators, marketing, or legal experts. The Semantic Suite links business objects and content assets automatically, extracting value from masses of data to make it actionable. It is easy to use, secure, and as simple to integrate as can be. Its user-friendly interface allows users to seamless transition to the software, and its low-learning curve is supported by the PoolParty Academy, which will get you up and running with the software in no time.


Victoria Penker joined Semantic Web Company in 2022 in the role of Partner Success and Marketing Manager. She studied Comparative Literature, Iberian Studies and German Philology at the University of Vienna and has a diverse background in education, the startup industry and content creation.
victoria.penker@semantic-web.com

Angela DaSilva is Content Strategist and Associate Director of Marketing at Semantic Web Company. Previously, she worked as a technical writer and a communications specialist in the software and government fields. She holds a BA in English Language and Literature and in Public Relations from Rhode Island College.
angela.dasilva@semantic-web.com

Lexicala by K Dictionaries is a technology partner of Semantic Web Company.
